What is your dosing strategy?
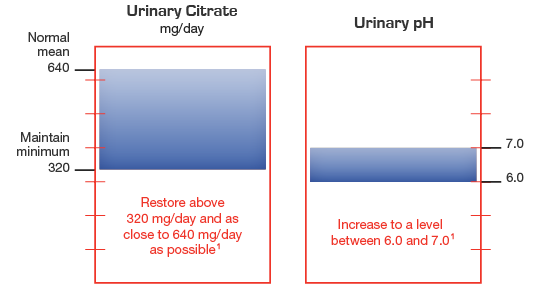
Therapeutic goals include raising urinary citrate and increasing urinary pH

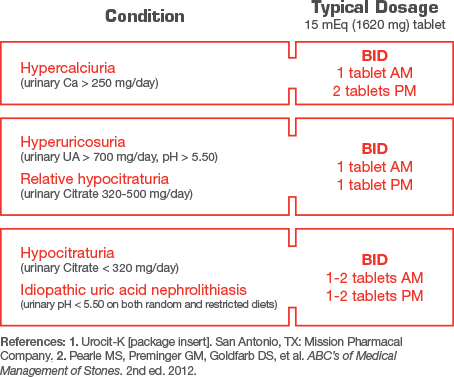
Provide a maximum-strength tablet for multiple conditions
Treatment with extended-release potassium citrate should be added to a regimen that limits salt intake (avoidance of foods with high salt content and of added salt at the table) and encourages high fluid intake (urine volume should be at least 2 liters per day). Urocit-K 15 mEq (1620 mg) should be taken with meals or within 30 minutes after meals or bedtime snacks.
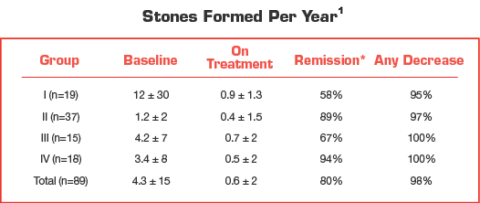
Urocit-K treatment outcomes
Effect of Urocit-K in patients with calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis1
*Remission defined as “the percentage of patients remaining free of newly formed stones during treatment.” Group I: n=19 (10 renal tubular acidosis, 9 chronic diarrheal syndrome). Group II: n=37 (5 uric acid stones alone, 6 uric acid lithiasis and calcium stones, 3 type I absorptive hypercalciuria, 9 type II absorptive hypercalciuria and 14 hypocitraturia). Group III: n=15 (history of relapse on other therapy). Group IV: n=18 (9 type I absorptive hypercalciuria and calcium stones, 1 type II absorptive hypercalciuria and calcium stones, 2 hyperuricosuria calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis, 4 uric acid lithiasis accompanied by calcium stones and 2 hypocitraturia and hyperuricemia accompanied by calcium stones).
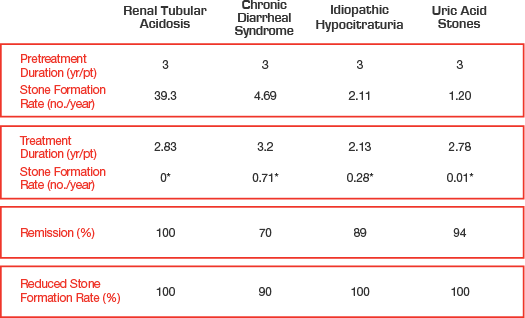
Manage a variety of kidney stone conditions
Urocit-K 15 mEq inhibits stone formation in more than 90% of
patients3,4,5
Urocit-K may benefit your patients
Prescribe maximum-strength Urocit-K 15 mEq for patients who may:
- Prefer taking fewer tablets per day which may help reduce pill burden


Urocit-K may benefit your patients
Prescribe maximum-strength Urocit-K 15 mEq for patients who may:
- Prefer taking fewer tablets per day which may help reduce pill burden
References: 1. Urocit-K [package insert]. San Antonio, TX: Mission Pharmacal Company. 2. Pak CYC, Fuller C, Sakhaee K, et al. Long-term treatment of calcium nephrolithiasis with potassium citrate. J Urol. 1985;134(1):11-19. 3. Preminger GM, Sakhaee K, Skurla C, et al. Prevention of recurrent calcium stone formation with potassium citrate therapy in patients with distal renal tubular acidosis. J Urol. 1985;134(1):20-23. 4. Pak CYC, Peterson R, Sakhaee K, et al. Correction of hypocitraturia and prevention of stone formation by combined thiazide and potassium citrate therapy in thiazide-unresponsive hypercalciuric nephrolithiasis. Am J Med. 1985;79(3):284-288. 5. Lipkin ME, Preminger GM. Demystifying the medical management of nephrolithiasis. Rev Urol. 2011;13(1):34-38.

